Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Naoe, Takashi; Wakui, Takashi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Teshigawara, Makoto; Haga, Katsuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2023-022, 81 Pages, 2024/01
In the liquid mercury target system for the pulsed spallation neutron source of Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), pressure waves that is generated by the high-energy proton beam injection simultaneously with the spallation reaction, resulting severe cavitation erosion damage on the interior surface of the mercury target vessel. Because the bubble of pressure wave-induced cavitation collapsing near the interior surface of the mercury target vessel with applying the large amplitude of localized impact on the surface. Since the wall thickness of the beam entrance portion of the target vessel is designed to be 3 mm to reduce thermal stress due to the internal heating, the erosion damage has the possibility to cause the vessel fatigue failure and mercury leakage originated from erosion pits during operation. To reduce the erosion damage by cavitation, a technique of gas microbubble injection into the mercury for pressure wave mitigation, and double-walled structure of the beam window of the target vessel has been applied. A specimen was cut from the beam window of the used mercury target vessel in order to investigate the effect of the damage mitigation technologies on the vessel, and to reflect the consideration of operation condition for the next target. We have observed cavitation damage on interior surface of the used mercury target vessel by cutting out the disk shape specimens. Damage morphology and depth of damaged surface were evaluated and correlation between the damage depth and operational condition was examined. The result showed that the erosion damage by cavitation is extremely reduced by injecting gas microbubbles and the damage not formed inside narrow channel of the double-walled structure for relatively high-power operated target vessels.
 Pb and
Pb and  Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeV
Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeVIwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Sugihara, Kenta*; 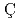 elik, Y.*; et al.
elik, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 544, p.165107_1 - 165107_15, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The lack of double-differential cross-section (DDX) data for neutron production below the incident proton energy of 200 MeV hinders the validation of spallation models in technical applications, such as research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs). The present study aims to obtain experimental DDX data for ADS spallation target materials in this energy region and identify issues related to the spallation models by comparing them with the analytical predictions. The DDXs for the (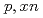 ) reactions of
) reactions of  Pb and
Pb and  Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30
Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30 to 150
to 150 using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.435 - 449, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:66.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) for Fe, Pb, and Bi targets induced by 107-MeV protons were measured using the fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator at Kyoto University for research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs) and fundamental ADS reactor physics research at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). Note that TTNYs were obtained with the time-of-flight method using a neutron detector system comprising eight neutron detectors; each detector has a small NE213 liquid organic scintillator and photomultiplier tube. The TTNYs obtained were compared with calculation results using Monte Carlo-based spallation models (i.e., INCL4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JQMD/GEM, and JQMD/SMM/GEM) and the evaluated high-energy nuclear data library, i.e., JENDL-4.0/HE, implemented in the particle and heavy iontransport code system (PHITS). All models, including JENDL-4.0/HE, failed to predict high-energy peaks at a detector angle of 5 . Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of
. Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of  20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
Saito, Shigeru; Suzuki, Kazuhiro; Obata, Hiroki; Dai, Y.*
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 34, p.101338_1 - 101338_9, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, a post-irradiation examination of pure tungsten (W) and tantalum (Ta) specimens irradiated at the Swiss Spallation-Neutron Source is conducted. W is used as a potential candidate for a solid spallation-target material owing to its favorable properties. However, W also suffers from several disadvantages such as poor corrosion resistance to water coolant and irradiation embrittlement. To improve these properties, cladding technologies using Ta for W alloys have been developed. In the present study, we investigated the irradiation effects on two tungsten materials, poly-crystal W (W-Poly) and single-crystal W (W-Sin), along with pure polycrystalline Ta. The tensile-test results revealed that W-Poly exhibited almost no ductility after irradiation of 10.2-35.0 dpa. W-Sin was irradiated up to 10.2 dpa and demonstrated 6% of total elongation (TE). With regard to Ta, TE decreased based on the increase in irradiation, reaching almost zero at doses of more than 10.3 dpa.
Iwamoto, Hiroki
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.24 - 29, 2022/03
Various spallation reaction models have been developed for the use of neutronic and shielding design of high-energy accelerator facilities such as J-PARC and ADS. However, their complicated theory for the de-excitation process has made improving their prediction accuracy difficult. In particular, it has been pointed out that the conventional models underestimate the yield of the spallation products produced from the fission reaction. This work has thus aimed to model the probability was described using a simpler, systematic expression, and then confirmed to predict fission cross sections for various incident energies and target nuclei with improved accuracy [1]. In this presentation, we will present the description of our model and research results. [1] H. Iwamoto and S. Meigo, "Unified description of the fission probability for highly excited nuclei", Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56:2, 160-171 (2019).
Ariyoshi, Gen; Obayashi, Hironari; Saito, Shigeru; Sasa, Toshinobu
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/03
To clarify the flow characteristics of heavy liquid-metal (HLM) is important to achieve the construction of nuclear transmutation facility that utilizes HLM as a spallation target and coolant. At present, lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) spallation target plans to be installed in Japan proton accelerator research complex (J-PARC). LBE is also selected as one of the candidate media of a spallation target and a coolant for innovative nuclear systems such as accelerator-driven system (ADS) and LBE-cooled fast reactor, due to its adequate physical/chemical properties. The characteristics of LBE flowing inside the target are usually clarified with computational fluid dynamics analysis since the measurement techniques for the HLM flow are not well established, especially for high temperature region over 450 C that is delivered from ADS's criteria. Therefore, the objective of this study is to develop measurement method for flow characteristics in the high temperature LBE. A miniature electro-magnet is introduced to electro-magnetic probe to overcome the limitation caused by a curie temperature of permanent magnet. To evaluate performance of the new probe, experimental apparatus equipping annular rotating vessel were also manufactured. The new probe was applied to high temperature LBE up to 480
C that is delivered from ADS's criteria. Therefore, the objective of this study is to develop measurement method for flow characteristics in the high temperature LBE. A miniature electro-magnet is introduced to electro-magnetic probe to overcome the limitation caused by a curie temperature of permanent magnet. To evaluate performance of the new probe, experimental apparatus equipping annular rotating vessel were also manufactured. The new probe was applied to high temperature LBE up to 480 C. As a result, proportional induced voltage to the rotation speed of LBE were clearly observed, where excitation currents of the miniature electro-magnet were 0.2 A or 1 A. In this paper, configuration and performance of the newly developed electro-magnet probe to the high temperature LBE will be presented.
C. As a result, proportional induced voltage to the rotation speed of LBE were clearly observed, where excitation currents of the miniature electro-magnet were 0.2 A or 1 A. In this paper, configuration and performance of the newly developed electro-magnet probe to the high temperature LBE will be presented.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita; Yee-Rendon, B.; Katano, Ryota; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Sasa, Toshinobu; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Research 2021-012, 58 Pages, 2022/01
A radiation shielding analysis was performed for the structure located above the spallation target of an accelerator-driven system (ADS), assuming one cycle of an 800 MW thermal and 30 MW beam power operation. In this analysis, the Monte Carlo particle transport code PHITS and the activation analysis code DCHAIN-PHITS were used. The structures to be analyzed are a beam duct above the target, a beam transport room located above the ADS reactor vessel, beam transport equipment, and the room ceiling. For each structure, the radiation doses and radioactivities during and after the operation were estimated. Furthermore, the shielding structure of the ceiling was determined. As a result, it was found that the radiation dose at the site boundary would be sufficiently lower than the legal limit by applying the determined shielding structure. Moreover, under the condition of this study, it was shown that the effective dose rate around the beam transport equipment positioned above the target after the operation exceeded 10 mSv/h, and that the maintenance and replacement of the equipment in the room would require remote handling.
Sasa, Toshinobu
Kasokuki, 18(4), p.233 - 240, 2022/01
Lead bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) is a promising option as a spallation target for accelerator-driven transmutation systems (ADS) to reduce the radiological toxicity from long-lived radioactive waste. LBE is a heavy metal and has suitable characteristics both as a spallation target and as a coolant for transmutation systems. However, LBE is also known as a highly corrosive with structural materials. In this paper, technological developments to overcome the issue, the latest research activities such as hightemperature operation and oxygen concentration control to ensure corrosion resistance, are introduced together with the outline of the target for ADS.
Haga, Katsuhiro
Kasokuki, 18(4), p.210 - 216, 2022/01
The pulsed spallation neutron source driven by a high-power accelerator is one of the most powerful apparatus to provide high intensity and high quality neutrons with narrow pulse width for conducting cutting-edge researches in several domains of materials and life science. In this system, proton beams of several kW to MW order extracted from the high power accelerator is injected into a target, which is heavy metal, to generate vast amount of neutrons via the spallation reactions with the target nuclei, and slows down these neutrons to thermal to cold neutrons with a moderator and a reflector. Resultant neutron beams are then supplied to a suit of the state-of-the-art experimental devices. In this paper, mechanism to produce neutron beams and outline of the spallation neutron source, engineering design of a target system such as a mercury target, and technical topics to solve the pitting damage problem of the target vessel which is caused by the pressure wave of up to 40MPa at maximum generated in the mercury by the pulsed proton beam injection are reviewed by referring mainly to the mercury target system of the pulsed spallation neutron source at J-PARC.
Takeshita, Hayato*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.30 - 41, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:64.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nuclide production cross sections for proton-induced reactions on Mn and Co at incident energies of 1.3, 2.2, and 3.0 GeV were measured by the activation method at the J-PARC. In total, 143 production cross sections of reaction products were obtained. Among them, the cross sections of  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) S and
S and  Mn(p,X)
Mn(p,X) Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
Ar were measured for the first time. The stable proton beam and well established beam monitoring system contributed to the reduction of the systematic uncertainties to typically less than 5%, which was better than those of the previous data. To examine the prediction capabilities of spallation reaction models and evaluated data library, the measured data were compared with the spallation reaction models in PHITS (INCL4.6/GEM, etc.), INCL++/ABLA07, and the JENDL/HE-2007 library. The comparison of the mean square deviation factors indicated that both INCL4.6/GEM and JENDL/HE-2007 showed better agreement with the measured data than the others.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita; Okubo, Nariaki; Yuyama, Takahiro*; Ishii, Yasuyuki*
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.296 - 301, 2021/10
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011046_1 - 011046_6, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
Sasa, Toshinobu; Saito, Shigeru; Obayashi, Hironari; Ariyoshi, Gen
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011051_1 - 011051_6, 2021/03
To realize Accelerator-driven system (ADS) for minor actinide transmutation, JAEA proposes to construct the Proton Irradiation Facility in J-PARC. The facility is planned to solve technical issues for safe application of Lead-bismuth Eutectic Alloy (LBE). The 250 kW LBE spallation target will be located in the facility to prepare material irradiation database by both proton and neutron irradiation in the temperature range for typical LBE-cooled ADS. Various studies for important technologies required to build the facilities are investigated such as oxygen concentration control, instruments development, remote handling techniques for target maintenance, and spallation target design. The large scale LBE loops for mock up the 250 kW LBE spallation target and material corrosion studies are also manufactured and applied to various experiments. The latest status of 250 kW LBE spallation target design works will be summarized.
Iwamoto, Hiroki
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (128), p.13 - 25, 2021/02
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.06001_1 - 06001_6, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.11(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Meigo, Shinichiro; Oi, Motoki; Fujimori, Hiroshi*
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(6), p.062802_1 - 062802_24, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:35.72(Physics, Nuclear)As hadron accelerators for such as the ADS and spallation neutron source achieve increasing beam power, damage to targets is becoming increasingly severe. To mitigate this damage, nonlinear beam optics based on octupole magnets is attractive. Nonlinear optics can decrease the beam-focusing hazard due to failure of the rastering magnet. As a side effect of nonlinear optics, the beam size is known to expand drastically compared with linear optics. Nonlinear effects have been studied via a simplified filament model that ignores beam-divergence spread at the octupole magnet. In this study, a new generalized model is proposed for application to an octupole magnet, regardless of the filament-model approximation. It is found that the transverse distribution obtained by beam tracking can be specified by the introduction of only two parameters, namely the normalized octupole strength of 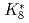 and the
and the 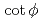 of the phase advance. To achieve the two antagonistic requirements of reduction of the beam-peak density and minimization of the beam loss, the transverse distribution is surveyed for a large range of beam position. It is found that a bell-shaped distribution with
of the phase advance. To achieve the two antagonistic requirements of reduction of the beam-peak density and minimization of the beam loss, the transverse distribution is surveyed for a large range of beam position. It is found that a bell-shaped distribution with 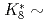 1 and
1 and 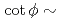 3 can satisfy requirements. This result is applied to beam transport in the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. The calculation result given by the present model shows good agreement with the experimental data, and the peak current density is reduced by 50% compared with the linear-optics case.
3 can satisfy requirements. This result is applied to beam transport in the spallation neutron source at J-PARC. The calculation result given by the present model shows good agreement with the experimental data, and the peak current density is reduced by 50% compared with the linear-optics case.
Saito, Shigeru; Okubo, Nariaki; Obayashi, Hironari; Wan, T.; Sugawara, Takanori; Sasa, Toshinobu; Maekawa, Fujio
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 28, p.071003_1 - 071003_6, 2020/02
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) proposes transmutation of minor actinides (MA) by accelerator-driven systems (ADS). The ADS designed by JAEA is a system composed by LBE (Lead-Bismuth Eutectic) spallation target and a subcritical core. In the ADS, a beam window (BW) is exposed in complex field of heavy irradiation by proton/neutron and corrosion by flowing LBE. To develop ADS structural materials, it is of critical importance to investigate materials used in such environment. Thus, JAEA plans to construct a proton irradiation facility at the J-PARC to prepare an irradiation database for candidate ADS structural materials and to investigate irradiation effects in flowing LBE environment. In this paper, giving a whole scope of the JAEA ADS development, some results of experimental measurements and the specific program for planed R&D will be presented.
Wakui, Takashi; Wakai, Eiichi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Naoe, Takashi; Hanano, Kohei; Haga, Katsuhiro; Takada, Hiroshi; Shimada, Tsubasa*; Kanomata, Kenichi*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 28, p.081002_1 - 081002_6, 2020/02
A mercury target vessel of J-PRAC is designed with a triple-walled structure consisting of the mercury vessel and a double-walled water shroud with internal and external vessels. During the beam operation at 500 kW in 2015, small water leakages from a water shroud of the mercury target vessel occurred twice. Design, fabrication and inspection processes were improved based on the lessons learned from the target failures. The total length of welding lines at the front of the mercury target vessel decreases drastically to approximately 55% by adopting monolithic structure cut out from a block of stainless steel by the wire-electrical discharge machining. Thorough testing of welds by radiographic testing and ultrasonic testing was conducted. The fabrication of the mercury target vessel #8 was finished on September 2017 and the beam operation using it started. Stable beam operation at 500 kW has been achieved and it could experience the maximum beam power of 1 MW during a beam test.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Takei, Hayanori; Matsuda, Hiroki; Yuri, Yosuke*; Yuyama, Takahiro*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.515 - 519, 2019/07
no abstracts in English
 Zr
ZrKawase, Shoichiro
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (122), p.75 - 80, 2019/02
Zirconium-93 is one of major long-lived fission products contained in high-level radioactive waste. This report introduces an experimental study of proton-and deuteron-induced spallation reactions on  Zr at 105 MeV per nucleon in inverse kinematics carried out at RIKEN RI Beam Factory. The isotopic production cross sections for a wide range of isotopes including stable ones were obtained. The experimental results were compared to the PHITS calculations considering both the intra-nuclear cascade and evaporation processes.
Zr at 105 MeV per nucleon in inverse kinematics carried out at RIKEN RI Beam Factory. The isotopic production cross sections for a wide range of isotopes including stable ones were obtained. The experimental results were compared to the PHITS calculations considering both the intra-nuclear cascade and evaporation processes.